The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is a cognitive ability test that measures a person's intellectual ability and cognitive strengths and weaknesses. The WAIS is a widely used intelligence test, which is designed to assess cognitive abilities in adults aged 16 to 90 years. It was first developed by David Wechsler in 1939 and has been updated several times since then to ensure its validity and reliability.
The WAIS measures various cognitive abilities, including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed. The test is made up of several subtests, each of which measures a different cognitive ability. The results of the subtests are combined to calculate a Full-Scale IQ score, which is a measure of a person's overall intellectual ability.
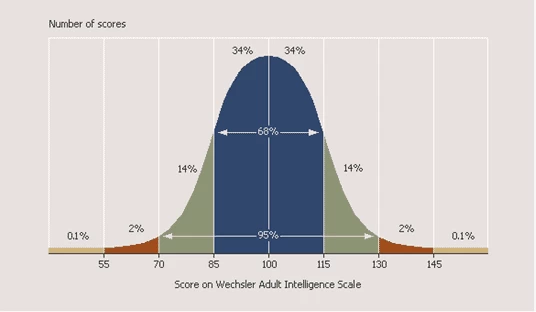
The Full-Scale IQ score is calculated using a standardization process, which involves comparing a person's performance on the test to that of a normative sample. The normative sample is a group of people who are similar in age and education to the person being tested. The average Full-Scale IQ score is 100, with a standard deviation of 15. This means that approximately 68% of the population has an IQ score between 85 and 115, and approximately 95% of the population has an IQ score between 70 and 130.
The WAIS has been used in a variety of settings, including schools, clinics, and research studies. It is often used to identify cognitive strengths and weaknesses, to diagnose cognitive disorders such as dementia or ADHD, and to assess cognitive functioning in people with neurological conditions such as stroke or traumatic brain injury.
It's important to note that the WAIS is just one measure of cognitive ability and should not be used as the sole determinant of a person's intelligence or potential. It's also important to consider other factors that may impact cognitive functioning, such as educational background, cultural differences, and environmental factors.
In conclusion, the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is a widely used cognitive ability test that measures intellectual ability and cognitive strengths and weaknesses in adults. The test is made up of several subtests and provides a Full-Scale IQ score, which is a measure of a person's overall intellectual ability. While the WAIS can provide valuable information about cognitive functioning, it should be used in conjunction with other measures and considerations to fully assess a person's cognitive abilities and potential.